Insertion Sort
The insertion sort is still relatively intuitive.
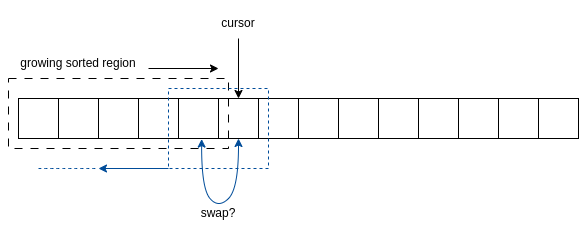
It works by:
- maintaining a sorted section on the left side of the array.
- a cursor iterates from left to right.
- In each iteration, an element is added to the sorted left side of the array.
- it works by repeatedly swapping the element with the preceding element until it is in order.
The insertion sort is:
- stable, equal elements maintain their relative order.
- in-place, it uses no significant extra memory to run.
- inefficient, having O(n^2) performance.
- not possible to run in parallel.
- works with non-numerical types, it uses a comparator.
For datasets that are already mostly sorted, the insertion sort can actually be more efficient on average than other algorithms.